
Article Summary: Flexible Printed Circuit Boards (FPC PCBs) are rapidly overtaking rigid printed circuits as the preferred interconnect solution for advanced electronics. From consumer devices to automotive systems, FPCs offer flexibility, lightweight packaging, high reliability, and cost benefits that traditional boards simply cannot match. This article explores the technology, benefits, industry applications, design considerations, and real world value of FPCs for modern device design.
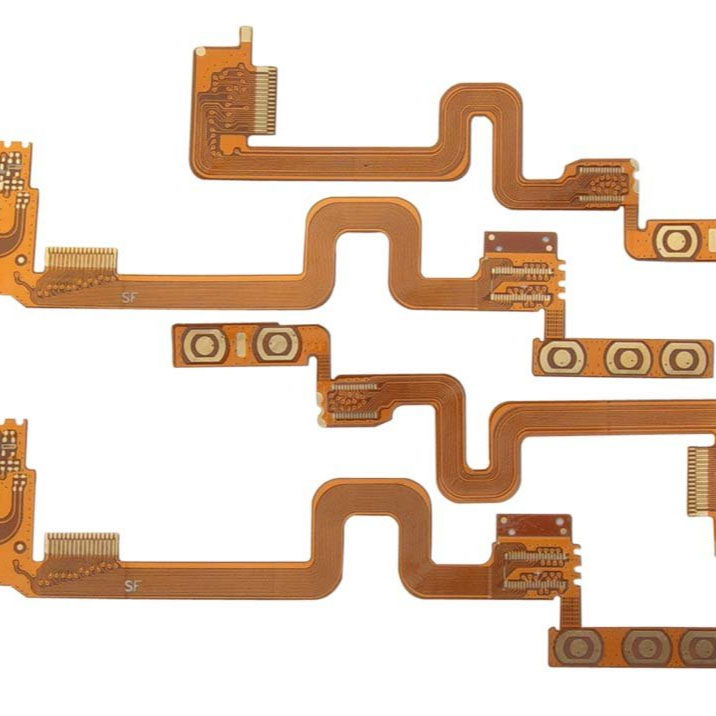
A Flexible Printed Circuit Board (FPC PCB) refers to a printed circuitry system fabricated on a flexible polymer substrate, such as polyimide or polyester, allowing the circuit to bend, twist, or fold without damage. It contrasts with traditional rigid boards that remain fixed and non‑bendable.
Unlike conventional rigid PCBs, FPCs are:
FPCs are manufactured using processes similar to standard PCB fabrication, with adaptations for flexibility:
After fabrication, components can be surface mounted, or connected via flex tails and special connectors.
FPCs can be up to 70% lighter and thinner than rigid boards, freeing up space in tight form factors.
Because FPCs bend and fold, they allow designers to innovate beyond flat circuit planes, supporting 3D layouts and compact assemblies.
The flexible substrate absorbs vibration and motion better than fixed substrates. Fewer connectors also reduce potential failure points.
FPCs often reduce the need for connectors, harnesses, and multiple boards. This simplifies manufacturing and reduces costs.
| Feature | Typical Material / Capability |
|---|---|
| Base Substrate | Polyimide / Polyester |
| Copper Thickness | 18–70 μm |
| Min Line Width | 0.05–0.1 mm |
| Layers | Single, Double, Multi‑layer |
These materials and processes ensure FPCs maintain flexibility while preserving electrical performance.
FPC use continues expanding alongside trends such as miniaturization, lightweight design, 5G connectivity, and wearables.
Effective design practices minimize stress, improve durability, and optimize performance for the specific application.
| FPC Flexible PCB | Rigid PCB | Rigid‑Flex PCB | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High | None | Moderate |
| Component Mounting | Limited | Strong | Best |
| Design Freedom | Excellent | Poor | Good |
Rigid‑Flex combines the strengths of both technologies but at higher costs. FPC offers unmatched flexibility for many compact, dynamic designs.
No. FPC PCBs are built on flexible substrates allowing bending and folding, unlike rigid PCBs that do not flex.
Polyimide and polyester are common flexible substrate materials.
FPCs can have higher unit costs than rigid boards, but overall system cost often decreases because they reduce connectors and assembly.
Depending on the material (e.g., polyimide), FPCs can withstand moderately high temperatures.
Today’s electronics increasingly demand smaller, lighter, and more dynamic interconnect solutions. FPC Flexible Printed Circuit Boards outperform conventional rigid PCBs in flexibility, design freedom, and system reduction, making them indispensable for modern device innovation.
When you need reliable, space‑saving, and high‑performance circuit solutions, trust the expertise of Akeson in advanced FPC manufacturing.
Ready to innovate with FPC technology? Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and access world‑class flexible PCB solutions!